Reflection and Practice on Promoting Forestry Innovation and Development with New Quality Productivity
The newly revised Forest Law of our country was implemented in July 2020, and Article 6 proposes that "the state aims to cultivate stable, healthy, high-quality, and efficient forest ecosystems, implement classified management of public welfare forests and commercial forests, highlight leading functions, give full play to multiple functions, and achieve sustainable utilization of forest resources", opening up the modern forestry development in China marked by the multifunctional management of forest ecosystems.

2023年9月在黑龙江考察期间,习近平总书记指出,要整合科技创新资源,引领发展战略性新兴产业和未来产业,加快形成新质生产力。深入理解新质生产力的科学内涵与发展路径,抓住新一轮科技革命和产业变革机遇,大力推进林业现代化产业体系建设,加快培育林业新质生产力,对于推进我国林业高质量发展具有重大战略意义。
How to implement the concept of "promoting forestry innovation and development with new quality productivity"? In recent years, the forest management team of Beijing Zhonglinlian Forestry Planning and Design Research Institute Co., Ltd., a member unit of the National Innovation Alliance for Forest Management, under the leadership of alliance expert Lu Yuanchang, has closely cooperated with experts from member units such as the Chinese Academy of Forestry and Beijing Forestry University through platforms such as the National Innovation Alliance for Forest Management and the Forest Management Engineering Technology Research Center of the National Forestry and Grassland Administration. They have conducted a series of specific explorations and practices on this topic, and have achieved some preliminary experience and results. Here is a brief summary for colleagues inside and outside the industry to refer to and discuss.

01 Scientific Principles for Forming New Quality Productivity
The core of developing new quality productive forces lies in innovation. The scientific mechanism of innovation is to expand the system elements and boundaries, construct new element relationships and system structures, promote the interaction between new and old system elements and traditional and modern technologies, thereby forming non-linear linkage effects of more element relationships and generating more and greater collaborative forces to promote the rapid development and progress of the overall system functions!
02 Basic ideas for forming new quality productivity in forestry
Specifically in the forestry industry, we believe that the basic characteristic of forestry is not a land cultivation system based on trees, but a multifunctional forest ecosystem management system that integrates human and nature. Therefore, understanding and utilizing the synergistic effect of management and natural forces is the essential feature that distinguishes the forestry industry from agriculture or other industries, and it is also the key focus of forming new quality productivity in forestry. To this end, we propose the basic idea of using the concept of collaborative management of forest ecosystems to support and form new quality productivity in forestry. It can be briefly expressed as a new forest management model that takes the overall multifunctional forest ecosystem as the management space, traditional and new system elements as the objects of action, human nature synergy as the mechanism of action, and is composed of a forest management technology system with near natural characteristics, which has the characteristics of supporting the development of new quality productivity in forestry.

Key points of reform to promote innovative development of forestry new quality productivity
The reform points of promoting innovative development of forestry new quality productivity through the concept of collaborative management of forest ecosystems can be expressed using the four main themes of "multifunctionality, near nature, full cycle, and full factor".
multifunctional
Multi functional forest management is a forest management approach that aims to simultaneously achieve two or more functions of forest supply, regulation, culture, and support at the forest stand or sub group level. This means compressing the scale of planned large-scale control and intervention in natural rotation period forestry management, and shifting towards a near natural management path focused on ecosystems, that is, the two types of management policies should be reformed and developed towards multifunctional management policies. Multi functional forests have the following characteristics:
Forests that simultaneously serve the four major functions of supply, regulation, culture, and support for two or more forests, and are constructed and cultivated entirely or partially through artificial sowing or seedling planting;
The tree species used for afforestation and replanting can be either non-native species adapted to the site or native species;
A forest stand can be composed of one tree species, a mixture of two tree species, or multiple tree species;
The age structure of forests can be single layered or multi layered of the same age.

near-natural
Near natural management is a forest management model designed based on the concept of natural forestry, refined forest ecosystem and landscape ecosystem scales, and basic control indicators such as near natural types and degrees, with different management intensities. The core value of it is the collaborative management of humans and nature in the direction of coordinated development of forest ecosystems. Therefore, under the requirements of new quality productivity, the design of forest products needs to be achieved in a mode of harmonious development between humans and nature, such as:
Forest nurturing and logging operations aim to obtain valuable timber on one hand, and on the other hand, provide more nutritional space for some dominant trees to continue growing faster and better;
When cultivating second-generation forest stands, medicinal crops, or creating forest landscapes by replanting seedlings under the forest canopy, if natural regeneration promotion is taken into account and full cultivation is avoided, operators can save labor and money, naturally benefit from the maintenance of diversity and the natural development of local plants, and the public can benefit from the improvement and beautification of various forest micro landscapes, water conservation, and rapid enhancement of carbon sequestration capacity and other ecological function progress;
The artificial introduction of edible fungi cultivation under the forest requires the treatment of symbiotic saprophytic large microorganisms with artificial assistance, allowing operators to obtain edible fungi while benefiting the forest ecosystem. This is reflected in the improvement of microbial diversity, litter decomposition, soil fertility, and overall vitality;
The construction of small and micro water sources with fire prevention and water use functions in forests can serve as both habitats and water sources for wildlife;
In the future, a considerable portion of forest ecosystems will develop well, with populations of plants, animals, microorganisms, and other species thriving. At that time, the limited use of some wild animals for hunting activities should also aim to maintain the vitality of natural forest regeneration and maintain the integrity and smoothness of the ecosystem's food chain, and so on.
Full cycle
Full cycle management is a technical concept of forest management discipline developed from the traditional concept of "forest management cycle" combined with the management needs of forest ecosystems with different age forest characteristics. In traditional forest management techniques, the management cycle refers to the interval between one harvest and another, mainly including the rotation period and the return year (also known as the cutting cycle). The rotation period is mainly used for the cyclical planning of single structure and function oriented timber forests, firewood forests, economic forests, and other forest species; The tropical year (selective cutting cycle) is used in the management of natural forests with different ages, which is the interval between two main cutting harvests according to the requirements of wood species or diameter grades; Their prominent feature is that they focus on the harvesting and utilization of the final product, while downplaying the cultivation and processing of other stages. In the context of ecological environment construction requiring the development of forests towards inter aged forest management, the traditional age group division technical indicators for artificial forest development can no longer meet the needs of practical work. Full cycle management breaks through the five age group stage limitations of planting mode characteristics, namely "young, medium, near, mature, and over", and understands and guides the management process from the five complete stages of overall forest ecosystem development, including "forest clustering, competitive growth, quality selection, near natural structure, and continuous forest structure". This forest development stage division index system is a new time index sequence for forest management, and its combination with the target diameter index of major tree species is one of the important technical indicators for achieving multifunctional forest ecosystem construction. Compared with traditional forest management techniques, the concept of "full cycle management" is also a management cycle, but there are improvements in the following two aspects.
In terms of time frame, it emphasizes the entire development process of forests as ecosystems under the goal of improving stability and growth capacity, rather than short-term processes guided by single utilization goals such as quantitative maturity and technological maturity, which is the time expression of the "principle of forest ecosystem integrity";
It covers various promotional management activities and operational treatments for the basic characteristics of various developmental stages of forests, not just harvesting and utilization operations, which is the expression of the "forest ecological technical principle". Therefore, in the full cycle management technology, the main cutting and utilization of mature trees is also one of the means to adjust forest structure and promote forest renewal.
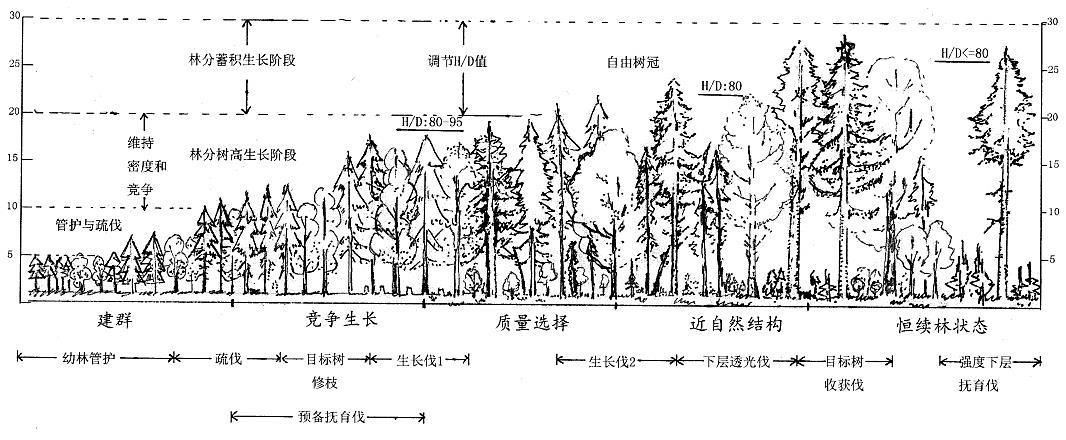
total factor
Total factor management is a technology of "human natural force" collaborative management that divides forest ecosystems into four subsystems: plant subsystems based on large trees, soil microbial subsystems based on microbial promotion, wildlife subsystems centered on small animals and birds, and system restrictive environmental subsystems focused on alleviating bottleneck factors. It is the structural decomposition and reorganization of forest ecosystems. Total factor management is an innovative forest management approach that uses a near natural approach to design comprehensive management measures based on the four core structural elements (subsystems) and relationships mentioned above, scientifically combining human management power with the natural growth power of forests to generate greater system level synergy and promote rapid forest growth and development.
Application Cases
The technical application areas of the concept of collaborative management of forest ecosystems include multifunctional management of artificial forests that balance ecology and production, conservation and management of natural forests, restoration of degraded forests, monitoring and evaluation of forest resource dynamics and management effectiveness, and innovative development in the Chinese model of forest health. The main features and manifestations are the multifunctional development of the ecological environment, material production, cultural landscape, and basic support (dual carbon strategy) of forest ecosystems, actively practicing the "Two Mountains" concept, innovating and coordinating the new forestry development concept of green openness and sharing, providing a technical route and application model based on trees and forest foundation for the construction of a community of life in the land ecosystem of mountains, waters, forests, fields, lakes, grasses, and sands. It is a new forest management theory and technical system that implements the ecological civilization construction concept of harmonious coexistence between humans and nature.
Case 1: Management of National Reserve Forest Ecosystem in Fujian Province by China Forestry Group
From June 2022 to June 2025, Zhonglin Union will provide technical training on national reserve forest ecosystem management innovation technology experiments and demonstration construction services to Zhonglin (Sanming) Forestry Development Co., Ltd. The expert group investigated and studied the natural and socio-economic characteristics and existing problems of the national reserve forests collected and stored by China Forestry Group in Sanming, Fujian. Based on typical forest management types, key technologies for improving forest ecosystem quality and nurturing management were proposed, and demonstration forest operation designs were carried out. The specific achievements include the "National Forest Reform Pilot Project National Reserve Forest Quality Improvement Technical Plan", "National Forest Reform Pilot Project National Reserve Forest Eucalyptus Degradation Forest Restoration Demonstration Forest Operation Design", "National Forest Reform Pilot Project National Reserve Forest Masson Pine Forest Ecosystem Management Demonstration Forest Operation Design", "National Forest Reform Pilot Project National Reserve Forest Precious Tree Species and Short term Crop Application Technology Demonstration Forest Operation Design", etc. During the implementation period, the project expert group, both internally and externally hired short-term experts, visited the site several times to conduct technical training, guidance, and discussions on the development of related industry models.
Case 2: Precise Improvement of Forest Quality in Beijing's National Public Welfare Forests
In order to comprehensively enhance the economic, social, and ecological value of the forest ecosystem in Beijing's mountainous areas, the Beijing Municipal Bureau of Landscape and Greening commissioned the China Forestry Federation to launch the "Beijing National Public Welfare Forest Quality Precision Improvement Standard Demonstration Zone Planning and Management Plan Compilation" in 2017. The project features the establishment of a new multi-functional management technology system for forest ecosystems, focuses on typical forest type management demonstrations, and requires the promotion of technology to the actual application of annual nurturing and management in mountainous areas throughout the city. With the support of the Forest Ecological Benefit Compensation Fund, it has been continuously implemented until now. This work is guided by the theories of "integrity", "comprehensiveness", "scientificity", "correlation", and "practicality" in systems engineering. Based on the deconstruction and reorganization of forest ecosystems through system engineering analysis, the forest ecosystem is divided into the four subsystems mentioned above. The technical research aims to achieve rapid improvement of the system through collaborative efforts between elements and subsystems. A key technical system for forest ecosystem management in Beijing, consisting of four key technical subsystems, is developed and demonstrated, which takes into account the landscape (small watershed) - forest stand - single tree scale. The innovation points are mainly reflected in the construction of a technical system for precise nurturing and management of all elements of Beijing's forest ecosystem, the establishment of a systematic engineering system for integrated forest management technology and management throughout the entire process of "job design technical construction inspection and acceptance input standards", and the construction of a multi-level integrated management technology system of "landscape forest stand single tree".

Case Three: Technical Guidance and Effectiveness Monitoring for Improving Forest Quality in Guizhou Province
Entrusted by the Forestry Bureau of Guizhou Province, we provide technical guidance and effectiveness monitoring services for improving forest quality throughout the province (2022-2024). Based on the overall requirements of adjusting tree species structure to improve forest quality in Guizhou Province, we provide technical support services to six pilot counties including Xishui County and Zhijin County. Specifically, it includes guiding pilot counties to develop implementation plans (homework designs) for pilot work; Each pilot county shall propose the classification of main forest management types based on specific circumstances and conduct demonstration plots (in small groups) for operational demonstration; Develop a pilot monitoring plan and compile monitoring data for report preparation. By the end of 2024, a comprehensive monitoring report for the entire province will be submitted, selecting forest quality improvement models that are suitable for Guizhou Province, and compiling the "Exploration of Forest Quality Improvement Paths in Guizhou Province (Initial Name)".

Case 4: Multi functional Forest Ecosystem Management of Yulin National Reserve Forest in Guangxi
The project takes the construction of national reserve forests in Yulin City as the carrier, and proposes a technical implementation plan for the transition from traditional management to forest ecosystem management of artificial commodity pure forests such as eucalyptus trees in the source areas of Nanliu River, Jiuzhou River, and Beiliu River in Yulin City. By improving the management of key elements and system relationships of multifunctional forest ecosystems in water source forests, while continuing to enhance ecological support functions such as water conservation, the forest structure is improved and forest quality is enhanced. The project implements business types and operation modes such as "eucalyptus+precious tree species+edible fungi" through innovative design, increases the reserve of high-quality wood resources, promotes the development of industries such as star anise, cinnamon, oil tea, and agarwood, and is of great significance for promoting rural revitalization and high-quality socio-economic development in Yulin City. Currently, due to the long-term pursuit of forest economic benefits, most commercial forests in Guangxi are pure forests of eucalyptus, pine, and fir trees. The forest structure and community structure are relatively simple, and the degradation of forest resources and land cannot be effectively achieved solely through precise nurturing operations. Yulin City took the lead in introducing the concept of forest ecosystem management in the construction of national reserve forest projects, and innovatively carried out the pilot construction of multifunctional forest ecosystem management. It is reported that the application of the project's management design and operational concept in the construction of Guangxi's national reserve forest is the first of its kind, providing new ideas and directions for the future construction of Guangxi's national reserve forest.

With the gradual deepening of China's social ecological civilization construction, it can be foreseen that the subsequent construction of a multi-functional value product system engineering system for national forest storage will be carried out with the support of the new concept of biodiversity economics, further expanding the connotation and boundaries of the system. Therefore, further promoting and implementing the collaborative management technology system of forest ecosystems will create greater ecological, economic, and socio-cultural value in serving the construction of national ecological civilization and the development process of the century old changes.
Disclaimer: The above content is sourced from the internet and the copyright belongs to the original author. If there are any copyright issues with the work, please let us know and we will handle them promptly!