Industry News | 2025 International Hydrogen Powered Ship Development Status
The combination of hydrogen energy and fuel cell technology is a major strategic direction for the world's energy and power transformation, and an important strategic measure to effectively address global energy shortages and reduce environmental pollution. Hydrogen fuel cells can be used as both propulsion and power sources for ships, and are suitable for ships such as ferries, supply ships, patrol ships, cargo ships, and sightseeing ships. Compared to other energy solutions, hydrogen fuel cells have the characteristics of high efficiency, no pollution, and low noise, and will become one of the preferred power sources after internal combustion engines.
At present, developed countries and regions such as the European Union, Japan, and the United States have mastered core technologies related to hydrogen energy and fuel cells, and have begun to implement multiple demonstration projects including hydrogen powered ships, taking the lead in promoting the industrialization and commercialization of hydrogen powered ship manufacturing.

·Progress of Global Hydrogen Powered Ships
European Union
The EU was the first to implement the hydrogen energy strategy deployment, with governments of various countries promoting the research and demonstration of fuel cell technology for hydrogen powered ships, taking the lead in occupying the technological high ground of the global industrial chain. The EU Hydrogen Strategy has been officially released, covering the entire industry chain of hydrogen production, storage, and transportation, as well as existing natural gas infrastructure, carbon capture and storage technologies, with a total investment of over 450 billion euros. In the development of hydrogen powered ship technology, the EU regards fuel cell and energy storage technology as strategic high-tech, and promotes related terminal applications through multiple investment projects. In terms of supporting construction for hydrogen powered ships, the EU plans to establish an open hydrogen market by 2030 to meet the demand of hydrogen powered ships for ports, docks, hydrogen refueling station networks, and large-scale hydrogen storage equipment. In addition, the governments of Germany, Norway, and France are vigorously promoting the establishment of energy simulation laboratories and increasing subsidies for hydrogen energy technology and infrastructure under the framework of the Energy Fund.
Japan
Japan actively promotes industrial collaboration, focusing on the research and development of large ocean going hydrogen powered ships and engines, and building a complete industrial chain development of hydrogen powered ships as a whole. Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Yangma Power, and Japanese Engine Company jointly established HyEng, dedicated to developing hydrogen powered engine systems for ships, establishing international standards and regulations for hydrogen fuel supply systems, and maintaining and operating hydrogen fuel engine demonstration facilities. To promote the social application of hydrogen energy, companies such as Kawasaki Heavy Industries and Iwatani Materials of Japan have jointly established the "Zero Carbon Hydrogen Energy Supply Chain Technology Research Association (HYSTRA)" to carry out research and development on hydrogen energy application, liquid hydrogen transportation and storage technologies. The full industry chain empirical experiment of liquefied hydrogen "manufacturing transportation unloading storage" has been completed, and it is expected to achieve the commercialization goal of the hydrogen energy supply chain by 2030.

America
Hydrogen and hydrogen based fuels are excellent solutions for carbon reduction and decarbonization in the shipping industry, and their application scope will gradually expand with the maturity of fuel application technology and the improvement of supporting facilities. Hydrogen powered vessels are commonly used in lakes, inland rivers, nearshore areas, and other scenarios, mainly including passenger ships, ferries, inland cargo ships, tugboats, and other types; The development of large hydrogen powered vessels such as offshore engineering ships, offshore roll on/roll off ships, and super yachts is currently an international trend, and submarines using hydrogen fuel cell power systems also have good prospects.
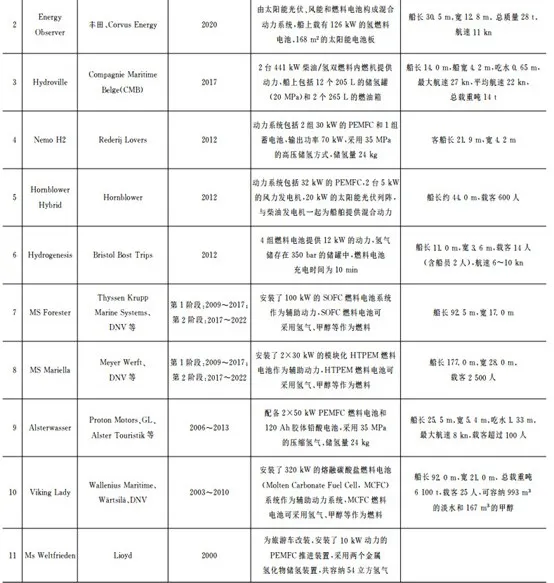
At present, hydrogen fuel cells are suitable for various inland ships, serving as the main power source for small vessels and as an auxiliary power source for large vessels; The proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) is the main type, and its power level has a significant gap compared to traditional diesel engines. Developed countries have successfully developed different types of hydrogen powered ships and achieved demonstration application effects, such as the German "Alsterwasser" cruise ship, Japanese fuel cell fishing boat, French "Energy Observer" yacht, American "Water Go Round" ferry, South Korean "Gold Green Hydrogen" hydrogen powered tourist boat, etc; Further research and application will be carried out, such as the Norwegian "Ulstein SX190" offshore engineering ship, "Topeka" roll on/roll off ship, and the Italian "ZEUS" test ship (see figure below).

The power technology of hydrogen fuel cells continues to develop, but the high integration and high-power hydrogen fuel technology for ships still needs breakthroughs
At present, the power of a single group of fuel cells for hydrogen powered ships is 100 kilowatts. When shipping, multiple groups of fuel cells are usually cascaded. For example, "Alsterwasser" cruise ships are equipped with two groups of 48 kW PEMFCs, 214 submarines are equipped with two groups of 120 kW PEMFCs, and domestic "Green the Pearl River" inland cargo ships are planned to be equipped with four groups of 135 kW PEMFCs. The megawatt level fuel cell system, as a key development direction in the future, is the foundation for the widespread application of fuel cells on ships; The fuel cell systems used in the Topeka roll on/roll off ship and Ulstein SX190 offshore engineering ship have power outputs of 3MW and 2MW, respectively; Ballard Power Systems has developed a 200kW marine fuel cell module that can be used in up to 6 sets, meaning that the power of the fuel cell system can be expanded to 1.2 MW.
Ship fuel cell systems are usually equipped with batteries of a certain capacity to "peak shaving and valley filling" the output power of fuel cells. For example, the "Alsterwasser" cruise ship is equipped with a 201.6 kW · h battery, the "Water Go Round" ferry is equipped with a 100 kW · h battery, and the Dutch "AQUA" concept cruise ship has a battery capacity of 1.5 MW · h. A matching system model can be constructed based on the power demand of the ship, combined with the energy supply characteristics of fuel cells and batteries, to optimize battery configuration.
Based on long-term planning and layout of hydrogen energy and fuel cell technology, well-known foreign companies such as Ballard in Canada, PowerCell in Sweden, Panasonic in Japan, and Doosan in South Korea have all developed fuel cell products and are in a leading position in the research and application promotion of high-power fuel cell systems for ships. Among them, Ballard Canada is a leading global enterprise in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. The company has mastered core technologies such as fuel cell systems, membrane electrodes, and bipolar plates, and its fuel cell products have been widely used in the field of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles.
In recent years, Ballard has begun to expand its presence in the medium and heavy-duty power markets such as trucks, trains, and shipping, while constantly introducing new fuel cell products. In recent years, Ballard has launched high-power marine hydrogen fuel cell systems. The system consists of basic battery system modules of 200 kilowatts, which can be connected into larger power battery system module groups to meet the high-power application needs of ships.
Swedish PowerCell is a leading global manufacturer of fixed and mobile fuel cell stacks and systems. The company's fuel cell stack system is compact and adopts modular design, which has high competitiveness in the current fuel cell vehicle market. In recent years, PowerCell has launched a hydrogen fuel cell module system specifically designed for ships. The power of each module in the system is 200 kilowatts, and megawatt level power can be achieved through parallel connection. In addition, Panasonic of Japan and Doosan of South Korea are also carrying out high-power marine hydrogen fuel cell projects.
Overall, the power of marine hydrogen fuel cells is not high at present. For ships of ten thousand tons, their power demand is in the megawatt level, which is much higher than the kilowatt level demand of automotive systems. In the current situation where the power of a single battery is limited, a large number of battery cells are needed. Considering the limited space on board, the integration technology of high compact high-power hydrogen fuel cell systems for ships still needs to be breakthrough.
Famous foreign fuel cell companies

Europe, America, Japan, and South Korea have achieved demonstration and promotion of hydrogen fuel cells on small ships, but there are no demonstration cases of large ocean going ships yet
At present, countries such as France, Germany, Belgium, Japan, and South Korea have implemented pilot and application of hydrogen fuel cell systems for ships, launching multiple hydrogen fuel cell vessels. Representative ones include the French "Energy Observer", German "Alsterwasser", and Belgian "Hydroville". At present, most of the hydrogen fuel cell ships launched are passenger ships, and there are almost no demonstration applications of fuel cell technology on ocean going transport ships or other large vessels. This is because the current fuel cell technology has not yet met the requirements of large ocean going vessels for battery output power, range, and service life. Overall, it can be seen that hydrogen fuel cell ships are still in the early stages of development, and there is still a long way to go before they can be widely and extensively applied in the field of ships. But it cannot be denied that these completed hydrogen fuel cell ships will lay a solid foundation for the development of subsequent hydrogen fuel cell ships.
Hydrogen fuel cell ships have been built abroad

·The latest case of global green powered ships
650 million subsidies! Norway's green shipping launches new strategy, with hydrogen ammonia powered ships becoming the biggest winners
The Norwegian government recently launched a major funding program with a total amount of approximately 918 million Norwegian kroner (approximately 650 million yuan) aimed at promoting the low-carbon transformation of the maritime industry. This funding willFocus on supporting the research and construction of clean fuel ships such as hydrogen and ammonia energyThe green upgrade of supporting port facilities marks a substantial step forward for Nordic countries in sustainable shipping development.

In this round of funding, Enova, a funding agency under the Norwegian Ministry of Climate and Environment, announced that it will support the development and construction of four hydrogen powered ships and two ammonia powered ships. The hydrogen energy project received approximately 510 million Norwegian kroner (about RMB 360 million) in funding, while the ammonia energy project received 253 million Norwegian kroner (about RMB 180 million) in funding.
The world's first case! The rotor wind tube technology of liquid ammonia transport ship has been certified, with an annual emission reduction of over 1000 tons
The energy-saving solution for the rotor duct of the 93000 cubic meter ultra large liquid ammonia transport ship (VLAC) independently developed by China Shipbuilding Group Jiangnan Shipbuilding has recently received principle recognition (AIP) from Lloyd's Register (LR) in the UK, becomingThe world's first commercial application of this technology on liquid ammonia transport ships.

The dual fixed rotor wind duct scheme can meet the requirements of ship air height and optimize blind spot visibility, with an expected reduction of nearly 4% in main engine energy consumption and an annual carbon dioxide reduction of over 1000 tons per ship.
The world's first ship! Solar hybrid inland waterway cargo ship put into operation
Wattlab from the Netherlands and HGK Shipping Company from Germany recently put into operation the world's first solar hybrid inland waterway cargo ship, the Blue Marlin. The ship pioneered the use of 192 photovoltaic panels (peak power of 35kW) for both domestic electricity and high-voltage propulsion systems, becomingThe world's first inland waterway cargo ship to achieve photovoltaic direct drive propulsion.

Its intelligent energy management system collaborates with four diesel engines to achieve power "peak shaving", avoiding starting backup units during high loads and significantly reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Under light load downstream conditions, the ship can even achieve full solar navigation. Compared to the record breaking solar powered cargo ship "Helios" in 2024 (which only supports low-voltage household electricity), "Blue Marlin" marks a major breakthrough in hybrid ship technology.
Disruption of liquid carbon transportation! The start-up cost of the world's first dry ice carbon sequestration transportation chain has dropped by 60%
DecarbonICE, a Danish company, has pioneered the use of dry ice pellets (solid CO ₂) to construct a complete carbon transport chain, which costs only 1/20 of the transportation of liquid CO ₂. Recently, the company successfully completed a sea freight test from Denmark to Iceland using standard containers: 20 tons of dry ice were transported at -78.5 ℃ atmospheric pressure, with a daily sublimation loss of only 0.3%, and no need for pressurized refrigeration equipment throughout the entire process.

This technology enables seamless integration of truck, ship, and railway multimodal transportation, and containers can be mixed and transported without the need for a safety isolation zone. Although dry ice preparation requires additional costs, the overall transportation cost is reduced by 60% compared to liquid CO ₂ ships. At present, the company is advancing its first commercial project - transporting carbon dioxide captured by biomass power plants.
The four major maritime associations in the world jointly establish the Electrification Alliance, aiming for zero emissions from ships
The four major international maritime organizations - the International Electric Ship Association (IEMA), the Zero Emission Ship Technology Association (ZESTA), the Marine Battery Forum (MBF), and the European Shore Electricity Association (EOPSA) - have jointly launched the Global Maritime Electrification Alliance (GAME) to accelerate the electrification process of inland, nearshore, and commercial ships. The alliance covers over 250 institutions worldwide and will promote zero emission solutions through collaborative research, policy advocacy, and industry cooperation.
The chairman of the alliance emphasized:“Ship electrification has mature technology and is currently the most direct and scalable emission reduction path”. In response to pain points such as policy dispersion and infrastructure gaps, the alliance will take the lead in releasing joint white papers and deepening cooperation in strategic regions such as North America, Europe, and India. The President of the European Shore Power Association pointed out that 'shore power supply is the most direct decarbonization tool, and electrification transformation is an operational reality'.
Article source: China Hydrogen Innovation and Maritime Silk Road Port Cooperation Forum